Choosing a cybersecurity career is both rewarding and challenging. Learning cyber security offers numerous advantages, and professionals who learn, understand, prepare for, and mitigate cyber threats will be in demand in the job market.
The need for cybersecurity practitioners continues to rise, and the global cybersecurity job vacancy is projected to be nearly 4 million people, according to the Strategic Cybersecurity Talent Framework 2024 report published by the World Economic Forum.
Cybersecurity jobs allow people to start their careers without prior knowledge or experience in IT. Individuals who switch careers or are eager to learn cybersecurity from scratch can pursue several entry-level cybersecurity jobs in various career paths. Cyber security jobs salaries are quite satisfactory and promote a fair work-life balance.
In this blog, 7 entry-level cybersecurity jobs will be analyzed regarding the most sought-after certifications, yearly salary expectations, and future career prospects. Moreover, technical skills and strategies that prepare individuals to break into cybersecurity will be explored.

What Are 7 Entry-Level Cyber Security Jobs?
Here are the 7 entry-level cybersecurity jobs:
- Cybersecurity Analyst
- Security Operations Center (SOC) Analyst
- Cloud Security Analyst
- Incident Responder
- Penetration Tester
- Computer Forensics Analyst
- Security Auditor

There are various types of entry-level cyber security jobs available on the market. Cyber security jobs’ salaries vary depending on the job role, and each path offers different career projections.
Cybersecurity Analyst
Cybersecurity analysts, or information security analysts, are primarily responsible for preventing and mitigating cyber threats to protect data, systems, and networks. Entry-level cybersecurity analysts protect sensitive assets by recognizing vulnerabilities, implementing security measures, and conducting risk assessments. They should have basic knowledge in various areas, such as system administration, networking, frameworks, and malware analysis, for a more resilient security posture.
Relevant Certifications: CompTIA Security+, Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), GIAC Security Essentials Certification (GSEC), Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
Annual Salary: Average of US$99,400, according to ZipRecruiter.
Career Outlook: The cybersecurity analyst role is projected to grow by 33% between 2023 and 2033, which makes it the fifth fastest-growing profession, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics.
Security Operations Center (SOC) Analyst
SOC analysts monitor, investigate, and remediate cyber threats in real-time. Organizations can set up their own SOC teams or utilize outside services for robust and cost-effective security efforts. The term “cybersecurity analyst” is broader than “SOC analyst.” Entry-level SOC analysts mainly concentrate on threat monitoring and analysis, while cybersecurity analysts implement proactive measures to prevent potential threats.
Relevant Certifications: CompTIA Security+, Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), GIAC Security Essentials Certification (GSEC), Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
Annual Salary: Average of US$76,675, according to ZipRecruiter.
Career Outlook: After becoming an entry-level SOC analyst, there are multiple options as Tier 2 analyst, incident responder, threat hunter, or SOC manager. Additionally, they can switch to other job roles and adapt quickly since they have fundamental knowledge.
Cloud Security Analyst
Cloud computing is the future, as 96% of organizations utilize public cloud and 84% benefit from private cloud, according to the Cloud Computing in 2028: From Technology to Business Necessity report published by Gartner. Cloud security analysts protect the cloud infrastructures and resources. Entry-level cloud security analysts monitor network activities, prevent and mitigate cyber-attacks, manage backups, assess risks, and engage in identity and access management (IAM) activities.
Relevant Certifications: CompTIA Cloud+, GIAC Cloud Security Automation (GCSA), Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP), Certificate of Cloud Security Knowledge (CCSK)
Annual Salary: Average of US$107,334, according to ZipRecruiter.
Career Outlook: Cloud cybersecurity skills are highly sought-after, and organizations struggle to fill these roles. With a 46% demand, the cloud security skills gap is in the first position, according to the 2023 Cybersecurity Skills Gap Global Research Report published by Fortinet.
Incident Responder
Incident response is critical since cyber intrusions have adverse effects that are hard to compensate for. Cybersecurity incident responders try to identify, mitigate, and quickly recover from cyber incidents. They are also responsible for reviewing incident response plans and operating containing or eradication procedures. Incident responders leverage the latest tools and technologies to safeguard sensitive data, maintain business continuity, and reduce recovery time.
Relevant Certifications: Certified Computer Security Incident Handler (CSIH), GIAC Certified Incident Handler (GCIH), EC-Council Certified Incident Handler (ECIH)
Annual Salary: Average of US$116,028, according to ZipRecruiter.
Career Outlook: Incident responders can move into roles such as incident manager, chief information security officer, or other cyber security roles. Additionally, artificial intelligence (AI) will enhance the response and remediation capabilities.
Penetration Tester
Penetration testers simulate attacks and exploit vulnerabilities to identify weak points in systems or applications. Generally, penetration testing and vulnerability scanning are used interchangeably, but some differences exist. Pentesting utilizes human expertise to exploit vulnerabilities actively, while vulnerability scanning describes automated scanning efforts with tools. Entry-level penetration testers are also responsible for creating detailed reports showing vulnerabilities in the target.
Relevant Certifications: Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), GIAC Penetration Tester (GPEN), CompTIA PenTest+, Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP)
Annual Salary: Average of US$119,895, according to ZipRecruiter.
Career Outlook: The market size is about US$2.45 billion now and is projected to reach US$6.35 billion by 2032, according to 2024 Fortune Business Insights. Moreover, 85% of organizations plan to raise the pentesting budget, according to the State of Pentesting Report published by Pentera.
Computer Forensics Analyst
The field of digital forensics begins after an attack occurs. Computer forensics analysts collect evidence, investigate incidents, recover data, and interpret digital findings in terms of forensic science. They follow best practices such as data integrity and the chain of custody in every investigation step. Entry-level computer forensics analysts use advanced tools and reverse engineering techniques to detect and understand security breaches.
Relevant Certifications: Certified Digital Forensics Examiner (CDFE), GIAC Certified Forensic Examiner (GCFE), Certified Forensic Computer Examiner (CFCE)
Annual Salary: Average of US$101,672, according to ZipRecruiter.
Career Outlook: The global market for computer forensics is increasing rapidly. In 2023, the market value was about US$9.9 billion and is forecasted to reach US$18.2 billion in the following 5 years, according to MarketsandMarkets.
Security Auditor
Security auditors supervise and examine the security procedures and policies for system hardening. They assess the effectiveness of security control technologies and create reports on corrective measures. Entry-level security auditors enhance the overall security posture of the organization and ensure compliance with national and international standards and regulations by enforcing best practices.
Relevant Certifications: Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA), Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), CompTIA Security+
Annual Salary: Average of US$92,797, according to ZipRecruiter.
Career Outlook: The demand for cybersecurity auditors is rising. The global market value is now about US$3.34 billion, and it is estimated to reach US$5.3 billion by 2030, according to the 2024 report published by Pragma Market Research.
How to Prepare for an Entry Level Cybersecurity Job?
Individuals, whether starting from scratch or changing careers, can enroll in a cybersecurity course to prepare themselves for cyber security entry-level jobs. Cybersecurity courses incorporate theoretical knowledge, certification, and practical experience. Moreover, courses provide mentoring and networking support that boost the chance to land a job quickly. Furthermore, in addition to technical skills, gaining soft skills is necessary to prepare for an entry-level cybersecurity job.
Why Choose a Career in Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity jobs are gaining more importance as the threat landscape is getting more challenging. There are various reasons to choose a career in cybersecurity, such as career development opportunities, competitive salary, high satisfaction rate, and remote or hybrid working options. Entry-level cybersecurity jobs offer a good work-life balance, which makes them appealing to individuals. Moreover, people can break into the cybersecurity field without prior IT knowledge.
How to Break Into Cybersecurity Without a Degree?
Cybersecurity is popular and promising, but individuals are curious about the following question: How to start rewarding cybersecurity career path from scratch? The good news is that cybersecurity entry level jobs do not require any degree. Nowadays, recruiters value experience, certification, and skills more than degree programs.
Bootcamps are affordable and effective alternatives to traditional education with its extensive training in short time. Cybersecurity online courses present a job-focused curriculum supported by hands-on experience and industry-recognized certifications to help students land a job quickly.
What Certifications Are Beneficial for Entry-Level Cybersecurity Jobs?
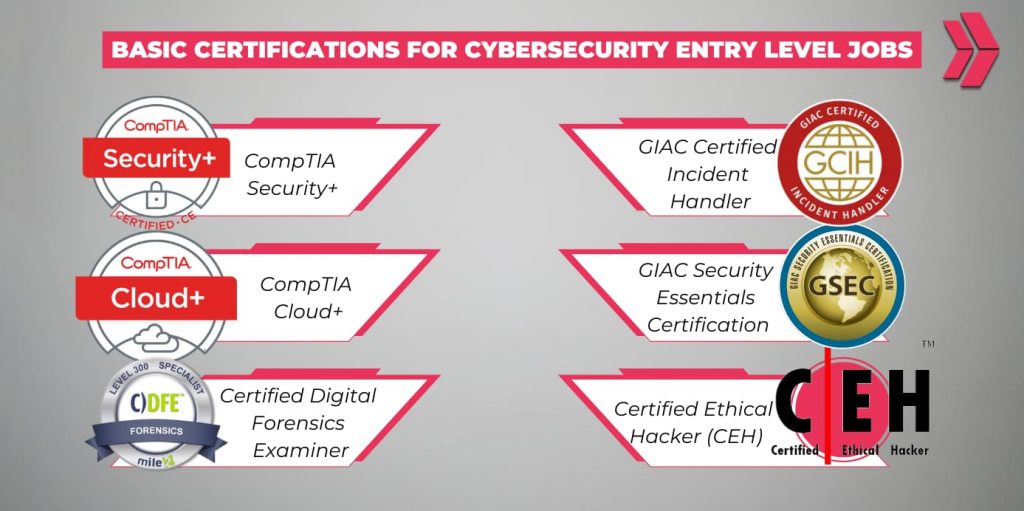
There are various cybersecurity certifications for different job roles. Here are some basic certifications for cybersecurity entry level jobs to consider: CompTIA Security+, Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), GIAC Security Essentials Certification (GSEC), CompTIA Cloud+, GIAC Certified Incident Handler (GCIH), Certified Digital Forensics Examiner (CDFE). Earning these cybersecurity certifications can significantly boost your qualifications and job prospects.
What Technical Skills Are Needed for Entry-Level Cybersecurity Jobs?
Essential cybersecurity skills help individuals understand basic security concepts and prepare them for the job market. Here are the 7 primary technical skills for an entry-level cybersecurity job: Operating systems and virtual machines, networking fundamentals, threat monitoring and incident response, risk assessment and vulnerability management, cybersecurity tools and applications, frameworks and compliance standards, and incorporating artificial intelligence (AI) into security efforts. Mastering these areas will significantly enhance your cybersecurity skills and readiness for the industry.
Conclusion
Individuals can change careers or start from scratch for entry-level cybersecurity jobs for numerous reasons, including vast career opportunities, high income, hybrid or remote working options, and satisfactory work conditions.
The cybersecurity field presents many job roles in various industries. There are 7 entry-level cybersecurity job roles worth exploring: Cybersecurity analyst, security operations center (SOC) analyst, cloud security analyst, incident responder, penetration tester, computer forensics analyst, and security auditor.
Professionals can break into cybersecurity without a degree or IT background. Cybersecurity bootcamps offer comprehensive training to pursue a career in cybersecurity. They provide the necessary knowledge and practical skills. Additionally, bootcamps prepare students for globally recognized certifications to acquire the essential skills. Cybersecurity courses also provide mentoring and career management support throughout the training to land entry-level cybersecurity jobs.




