As technology advances, security challenges and threat landscapes are also evolving. So, cybersecurity professionals must first learn and understand the diverse types of cybersecurity and then implement cybersecurity best practices to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of digital assets.
Learning cybersecurity is crucial for protecting digital data and privacy while fortifying defenses against cyber attacks. Cyber attacks globally surged by 7% in Q1 and 8% in Q2 2023 compared to the previous year, according to the 2023 Mid-Year Security Report published by Check Point.
This comprehensive overview provides insights into every cybersecurity career path to the multifaceted landscape of cybersecurity to prepare against potential threats.

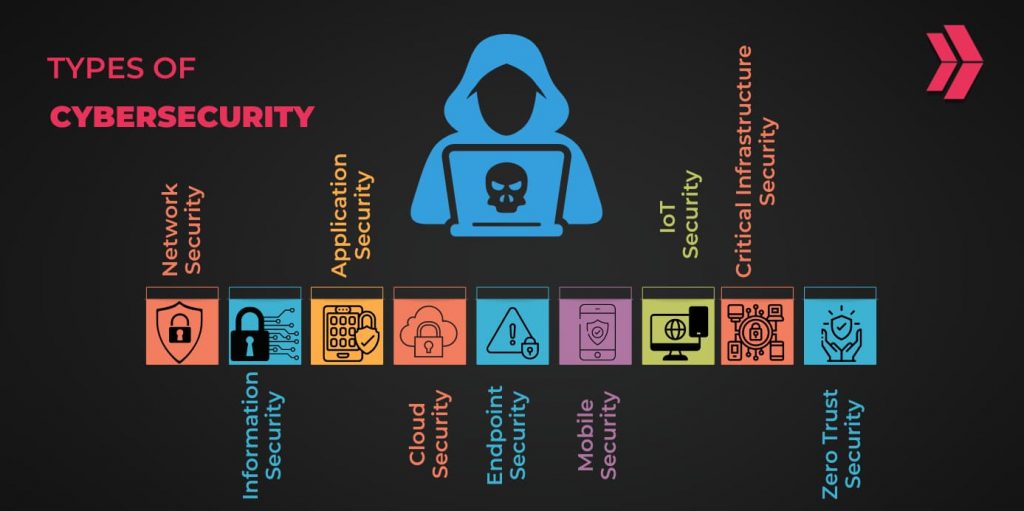
What Are the 9 Types of Cybersecurity?
To ensure the safety and security of information, organizations and individuals must consider the different types of cybersecurity available. Here are the 9 types of cybersecurity in safeguarding against cyber threats;
- Network Security
- Information Security
- Application Security
- Cloud Security
- Endpoint Security
- Mobile Security
- IoT Security
- Critical Infrastructure Security
- Zero Trust Security
1. Network Security
Network security is safeguarding computer networks from various types of cyber attacks. There are 6 main measures to ensure network safety: firewalls, security information and event management (SIEM) tools, virtual private networks (VPNs), network segmentation, sandboxing, and intrusion prevention systems.
2. Information Security
Information security focuses on keeping digital information safe. Some measures, including digital signatures, encryption, access control, security awareness training, and data backup and recovery, are highly effective in mitigating potential security breaches and other threats.
3. Application Security
Application security protects mobile applications, web applications, and other software programs from cyber intrusions. Application security measures encompass 4 primary efforts to protect valuable assets and data: secure coding practices, vulnerability assessments, patch management, and penetration testing.
4. Cloud Security
Cloud security refers to protecting sensitive data in the cloud environment. This concept tries to mitigate risks related to storage and system security in the cloud. There are 5 measures to secure cloud computing environments: access control, secure configuration, encryption, regular assessments, and data backup/recovery.
5. Endpoint Security
Endpoint security is a concept that responds to cyber threats against individual devices such as mobile devices, servers, desktops, and laptops. Businesses or organizations enhance the security posture by implementing security measures, including Endpoint Protection Platforms (antivirus, anti-malware), Mobile Device Management (MDM) for mobile devices, and Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR).
6. Mobile Security
Mobile security concentrates on protecting mobile devices and preventing mobile threats. Regarding mobile devices, 5 significant measures are beneficial to mitigate mobile cyber threats: Mobile Device Management (MDM, Mobile Application Management (MAM), encryption, patch management and updates, and strong authentication.
7. IoT Security
IoT security is paramount because IoT technology is exponentially growing in daily life and industrial areas. Also, attackers can exploit unsecured IoT devices as a vector for launching cyber attacks. Implementing basic measures such as a strong password policy, regular updates, and changing default settings can ensure IoT security.
8. Critical Infrastructure Security
Critical infrastructure security describes the precautions to ensure essential assets that are vital and directly affecting daily life. After identifying the inventory of critical assets, implementing some measures, such as access management, continuous monitoring, improving resilience and recovery plan, managing supply chain, and network segmentation, can enhance critical infrastructure security.
9. Zero Trust Security
The Zero Trust model never trusts by default and always requires verification before granting access to sensitive data. Security measures like continuous monitoring, encryption, micro-segmentation, least privilege access, and default deny access policies strengthen the model against cyber threats.
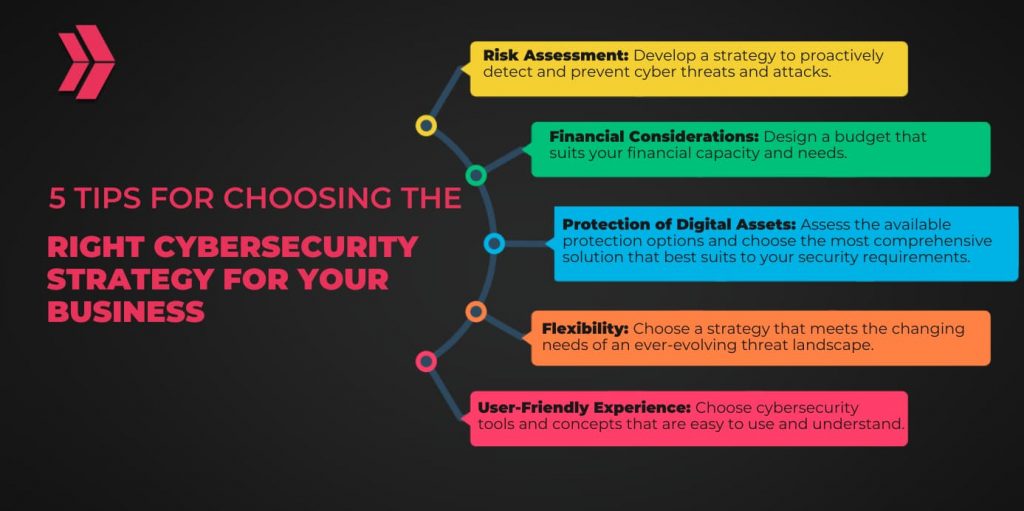
How to Choose the Right Cybersecurity Strategy for Your Business?
Choosing the right cybersecurity strategy for your business is vital to protecting your sensitive assets from cyberattacks. Here are 5 noteworthy tips to help you choose the right cybersecurity strategy:
- Risk Assessment: First, identify your business’s possible threats and attack vectors. Later, develop a robust strategy to pre-empt and prevent cyber attacks.
- Financial Considerations: Design a budget that aligns with your financial capacity and requirements.
- Protection of Digital Assets: Assess the available protection options and choose the most comprehensive solution that best suits and responds to your security requirements.
- Flexibility: Choose a strategy that meets the changing needs of the constantly evolving threat landscape since adaptability becomes more crucial than ever.
- User-friendly Experience: Choose cybersecurity tools and concepts that are easy to use and comprehend. Ensure that they are efficient while keeping things simple.
What are Common Cyber Threats?
The most common types of cyber threats include social engineering, malware, code injection, and DDoS (Denial of Services) attacks.
Social engineering, or human hacking, manipulates users to compromise sensitive information. Nearly all cyber attacks, around 98%, involve the use of social engineering techniques to carry out an attack, according to Purplesec report.
A malware is a code or program that aims to steal, modify, or disrupt the target. Globally, more than nearly 6 billion malware attacks occurred in 2022, according to Statista. The five most commonly used attack types are viruses, worms, trojans, ransomware, and backdoors.
Code injection attacks enable attackers to inject malicious code to manipulate the execution by exploiting vulnerabilities in the system. SQL Injection (SQLi) and Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) are the most common code injection attack types.
Denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks attempt to disrupt the normal functioning of the target and overwhelm the traffic by flooding it from multiple sources. Last year, DDoS attacks increased 150% globally compared to 2021, according to the Global Threat Analysis Report published by Radware.
Safeguarding against these diverse types of cyber attacks presents an ongoing challenge, requiring constant vigilance and adaptation to evolving threat landscapes.
What are the challenges of cyber security?
Cybersecurity challenges may vary depending on many factors, including industry, sector, and corporate culture. Businesses or organizations can face some challenges in cybersecurity, such as:
- The ever-changing nature of cyber threats requires being vigilant and up-to-date with emerging threats and best practices.
- The human factor is still the weakest link, so user training plays a significant role in overcoming human-related security challenges.
- Unfortunately, cybersecurity is often disregarded and considered an additional burden, although it is cost-effective.
- Limited resources, such as budget and personnel, hinder the implementation of the most efficient efforts.
- Weak configurations, inadequate password policies, and legacy or outdated systems can compromise security procedures and leave them vulnerable to attacks.
- Ineffective communication and lack of collaboration between individuals or teams can pose a significant challenge.
- Even the most advanced preventive measures cannot completely protect against security breaches, specifically when it comes to zero-day attacks.
- The rise of artificial intelligence and deep fake technology will be a force multiplier for attackers and harder to defend against.
What are cyber security best practices?
Cybersecurity best practices are strong password management, keeping software updated, recovery and backup plans, encryption, proper configuration, awareness of cybersecurity attacks, user training, and continuous learning. Cybersecurity experts use cybersecurity best practices to improve security posture and reduce cyberattacks.
How to start a Career Path in Cybersecurity?
Starting a career in cybersecurity is highly rewarding and offers various types of cybersecurity jobs. The cybersecurity industry presents numerous career paths to specialize in, so identifying the area of interest is crucial. After deciding about the cybersecurity career path, there are 5 key steps to follow:
First, a proper education is a good starting point for a successful career. Pursuing a formal college degree in cybersecurity or related fields increases the chances of landing a job. Alternatively, boot camps offer intense programs and practical experience that help individuals get a job quickly in a relatively short time.
Second, obtaining cybersecurity certifications verifies the level of knowledge and expertise in this field. Moreover, having a cybersecurity certification also increases the chances of being hired. In the hiring process, 82% of companies prefer candidates with certifications, as articulated by GIAC.
Third, having experience in the field gives you an edge over other candidates. While education and certification demonstrate theoretical knowledge, real-life experience proves practical skills.
Fourth, networking is essential in building relationships and creating opportunities for self-improvement. Also, networking is an excellent web of information sources and staying informed about the latest developments.
Fifth, continuous learning and staying up-to-date on the latest trends are not only necessary for personal and professional growth but also for responding and adapting to the evolving needs of the present times.
What are the Types of Cybersecurity certifications?
Cybersecurity certifications come in different types depending on your career path and level of expertise. Here are the top 10 cybersecurity certifications in the industry:
- CompTIA Security+,
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
- GIAC Security Essentials Certification (GSEC)
- Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP)
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
- Systems Security Certified Practitioner (SSCP)
- GIAC Certified Incident Handler (GCIH)
- CompTIA Advanced Security Practitioner (CASP+)
- Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA)
- Certified Information Security Manager (CISM)
In conclusion, as the digital landscape continues to evolve, understanding the diverse types of cybersecurity is crucial for safeguarding against the escalating threat landscape. This comprehensive overview highlights the nine key types of cybersecurity and provides valuable insights into securing information, applications, and critical infrastructure. The rise in cyber attacks emphasizes the necessity for robust cybersecurity strategies, making it imperative for businesses to choose the right approach. From common cyber threats to the challenges faced in the cybersecurity realm, the journey concludes with a roadmap for aspiring professionals, emphasizing the importance of education, certifications, experience, networking, and continuous learning in the dynamic field of cybersecurity. Armed with this knowledge, individuals and organizations can fortify their defenses, mitigate risks, and navigate the ever-changing cybersecurity landscape with resilience and confidence.




