In the digital era of 2024, cybersecurity is more than a buzzword—it’s a crucial shield against the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. With an estimated global cost of data breaches reaching a staggering $4.45 million, the urgency for robust cybersecurity measures is undeniable. This comprehensive guide illuminates the “Top 10 Cybersecurity Best Practices” that are imperative for IT professionals and organizations alike. By delving into these practices, we aim to fortify your digital assets against a variety of cyber risks, ranging from social engineering to sophisticated cyber-attacks.
Our exploration begins with the foundational step of using strong passwords, a seemingly simple yet powerful barrier against unauthorized access. We’ll then navigate through the multi-layered security of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), the critical importance of keeping software up-to-date, and the cunning world of social engineering attacks. Understanding these practices is not just about implementing strategies, but also about adopting a mindset of continuous vigilance and improvement.
From the essentials of regular data backups to the advanced realms of encryption and cybersecurity frameworks, each practice is a vital cog in the wheel of digital security. We also emphasize the pivotal role of continuous learning in staying abreast of the latest cyber threats and solutions. This guide not only presents these top 10 practices but also dives deep into their nuances, offering a blend of strategic insights and practical advice tailored for the dynamic world of 2024.
Join us as we embark on this crucial journey through the landscape of cybersecurity, where each practice is a step towards a more secure and resilient digital environment.

What are the Top 10 Cybersecurity Best Practices in 2024?
Cybersecurity best practices are vital to protect digital assets. By following these top-quality methods, IT professionals can contribute to improving the overall security posture and reduce the risk of cyber incidents. Here are the top 10 cybersecurity best practices:
- Use Strong Passwords
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Keep Your Software Up to Date
- Be Aware of Social Engineering Attacks
- Back-up Your Data
- Use a Firewall
- Encrypt Your Data
- Educate Your Employees
- Implement Cybersecurity Frameworks
- Continuous Learning

Let’s dive in together to see how these best practices enhance security:
1- Use Strong Passwords
Using strong passwords is the first line of defense and enhances security. On the other hand, weak passwords enable cyber intruders to gain unauthorized access to sensitive assets.
IT professionals should follow these tips for creating strong passwords:
- Passwords should include numbers, upper and lower case letters, and special characters.
- Using personal information such as birthdays, usernames, or email addresses would make you an easy target for cyber attacks.
- Avoid using guessable common words vulnerable to “dictionary attacks.”
- The passphrase is the new password for authentication. It is more secure and more prolonged than traditional passwords.
- Using different passwords for different accounts will eliminate the possibility of disclosure. And protect your other accounts if one of them is exposed.
- Moreover, password management tools are good options for generating and storing strong passwords and improving security.
2- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is the practice of providing at least two different verification factors in the account login process.
Furthermore, the MFA implementation provides an extra layer of security. Even if you experience password theft and your password is exposed, the MFA keeps you safe against cyber criminals.
MFA Authentication has 3 primary categories of methods: password or pin, badge or smartphone, and fingerprint or face recognition.
MFA enables IT professionals to improve identity and access management (IAM) policies. One of the most common MFA factors is a combination of a username-password and a one-time password (OTP) code sent to mail or mobile phone restricted to a limited time.
3- Keep Your Software Up to Date
Keeping software up to date is paramount to detect security flaws, take measures against vulnerabilities, and reduce attack surfaces.
IT professionals should ensure all software is updated with the latest security patches because cyber criminals could exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software.
Patch management helps increase productivity, lower costs, and comply with standards and regulations. Patch management practices mitigate cyber threats when appropriately implemented.
Automatic updates and vulnerability management protect your cyber environment by applying fixes issued by manufacturers. Automatic updates are essential for critical systems.
Automatic updates can be proactive in protecting against software vulnerabilities, but they may only sometimes be sufficient. For example, “zero-day attacks” can target vulnerabilities that antivirus or software vendors are unaware of. However, deploying timely updates or patches can help mitigate these attacks and offer additional data protection.
4- Be Aware of Social Engineering Attacks
Be Aware of Social Engineering Attacks is a crucial call to action in today’s digital landscape. Social engineering refers to manipulating and exploiting human nature to compromise sensitive information. Social engineering cyber attacks use psychological manipulation and “human hacking” rather than technical hacking.
There are many types of social engineering attacks cybercriminals are using such as phishing, pear phishing, pretexting, smashing, and watering hole attacks. Similarly, scammers use various techniques to deceive their targets. Attackers trick users into obtaining money directly or sharing personal information/credentials, although the attack type varies accordingly.
As an IT professional, detecting social engineering attacks is possible by paying attention to certain clues. For instance, if you receive generic greetings or signatures, unexpected calls or emails claiming to be an emergency, or suspicious requests that don’t align with your daily routine, it’s possible that you’re being targeted. Additionally, It’s important to exercise caution when receiving emails with unfamiliar attachments or URLs.
Besides, there exist various tools that can aid in mitigating the impact of social engineering attacks to a certain degree.
The Internet Crime Report published by the FBI declares that phishing attacks are the most common social engineering technique. An example is when someone posing as a bank employee calls and asks you to change your password immediately due to a security breach.
5- Backup Your Data
Backuping your data is vital for recovering data from various failures, including human error, computer or network systems, natural disasters, or cyber-attacks. Regular backups can mitigate data failures and ensure business continuity.
There are three main data backup types: full backup, incremental backup, and differential backup. First, full backup, a full copy of all files. Second, incremental backup, copying files that differ from the previous document. A third, differential backup, copying files different from the last full backup.
IT professionals can benefit from some of the following backup methods and strategies:
- Planning scheduled or automated backup processes.
- Using external hard drives or storing on a separate network in the backup process.
- Using cloud backup services as a managed network security.
- Checking regular backups for testing integration and working status.
In the modern world, cloud backup services offer many advantages. Local backups in external hard drives or on-premises are vulnerable to physical effects. Furthermore, cloud computing reduces costs and the space required for installation. Similarly, it offers easy access from anywhere, anytime.
To learn more about data migration and backup tools you can read the “Data Migration Tools (Open Source, On-Premise And Cloud-Based)” blog post.
6- Use a Firewall
Firewalls are crucial in monitoring and filtering network traffic based on specific parameters. With a zero trust policy, they offer strong security measures and adaptability. It is imperative to prioritize their implementation for a robust security framework.
Three main types of deployment models are available for firewalls. First, Hardware-based firewalls work as a secure gateway and are suitable for large groups of users. Second, Software-based firewalls are installed on and protect only one device. Third, cloud firewalls are another type of firewall that is hosted on the cloud.
Firewalls should be appropriately configurated for the most effective use and to avoid potential security risks. The best practices for firewall configuration are as follows:
- Implement the least privilege policies to minimize the attack surface.
- Set well-defined firewall rules and policies.
- Update the firewall regularly for better protection.
- Conduct regular firewall security audits and use loggings.

An excellent way to segment a network is through firewall segmentation, where all traffic is routed through the firewall at the network boundary. Access controls and firewalls should be well-balanced to regulate network segmentation and ensure optimal security.
7- Encrypt Your Data
Enhancing security measures by incorporating data encryption is crucial, as it safeguards sensitive information and privacy. Additionally, it allows for secure sharing and transfer of files. Data encryption keeps your data secure even if your device is lost or stolen.
Encryption algorithms consist of 2 methods: symmetric and asymmetric encryption. In symmetric encryption, only one key is utilized in encryption and decryption processes. On the other hand, in asymmetric encryption, a public key and private key pair in the whole encryption process. 3DES, AES, RSA, and Blowfish are among the most secure encryption techniques used in the industry.
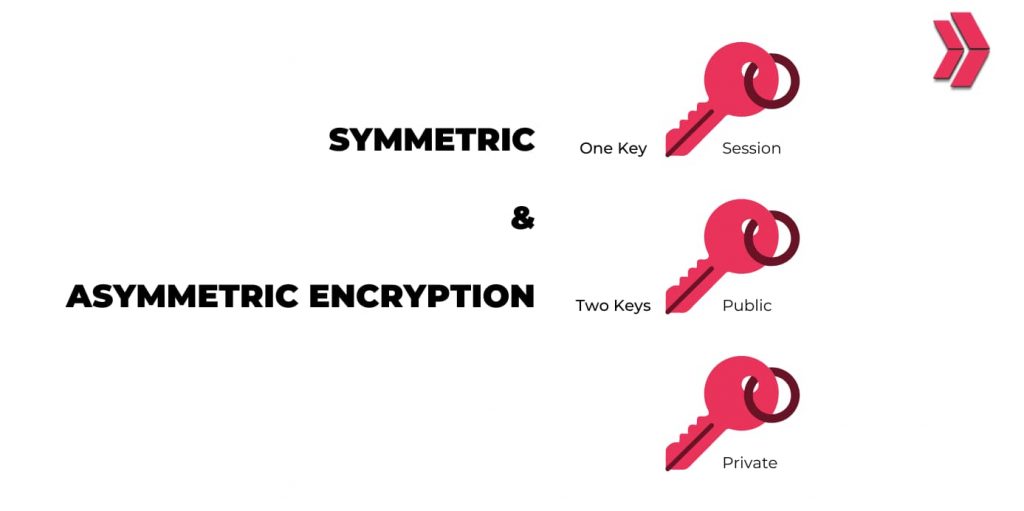
There are various encryption tools available in the market that provide secure solutions for protecting data. These tools cater to the needs of both individuals and organizations and are available in both paid and free versions.
Encryption technology is rapidly evolving. Quantum cryptography will shape the future of encryption and is expected to dominate information security.
8- Educate Your Employees
The human factor is still the weakest link in cybersecurity incidents. According to Verizon’s 2023 Data Breach Investigations Report, the human element is responsible for 74% of data breaches by misuse, errors, or social engineering attacks.
Cybersecurity awareness training is crucial to introduce the threat landscape. It teaches how to recognize cyber attacks such as phishing, malware ransomware, and DDoS. These trainings create a culture of security in the work environment and raise awareness of cyber threats.
IT professionals should have regular cybersecurity awareness training to take necessary measures to avoid them. From this perspective, a training program for company employees is significant to understand cyber criminals’ tactics, techniques, and procedures.
Furthermore, education makes IT professionals more attentive to details to detect potential threats and more proactive in cyber threat reporting and incident response procedures.
9- Implement Cybersecurity Frameworks
Cybersecurity frameworks are the guidance and best practices to enhance the security posture. Organizations utilize this set of policies, practices, and procedures to preempt and prevent security breaches.
Cybersecurity frameworks help organizations identify, evaluate and manage security risks. Consequently, they provide a course of action to assess, develop and maintain security measures.
Furthermore, cybersecurity frameworks guarantee adherence to state, industry, and international regulations. Properly implementing these frameworks can also prevent fines and penalties resulting from data breaches.
When organizations implement frameworks, they establish consistent standards for effective communication. This enables them to use a common language and work together more efficiently.
Numerous frameworks are utilized to minimize the risks of cyber threats, including the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, ISO 27000, Series, specifically ISO 27001, GDPR, and MITRE ATT&CK. These frameworks safeguard essential assets.
10- Continuous Learning
As cyber-attacks evolve, IT professionals must stay updated with the latest threats and best practices to keep up with the changing threat landscape. Learning is a lifelong process requiring individuals to be self-motivated to pursue new knowledge.
Likewise, IT practitioners should frequently revise and improve their policies and procedures to maintain an effective defense against security breaches.
Attending cybersecurity conferences and webinars is an excellent way to stay up-to-date on industry trends and expand your professional network. These events offer excellent opportunities to broaden your horizons.
Cybersecurity certifications are excellent for ongoing learning—curriculum changes align with the market’s needs. Also, credentials should be updated due to expiration, which keeps practitioners current.
Self-improvement can be achieved through cybersecurity boot camps or training programs that provide excellent learning and development opportunities. Attending workshops is a great way to improve learning and develop new skills for overcoming industry-related challenges.
Why is Cybersecurity Important?
Cybersecurity is critical because it protects sensitive data, prevents unauthorized access that leads to huge costs, and maintains trust and a good reputation between parties in an increasingly digital world.
First, cybersecurity efforts protect sensitive data like Personally Identifiable Information (PII), intellectual property, Protected Health Information (PHI), trade secrets, and other sensitive data against cyber attacks or cyber espionage.
In addition, implementing cybersecurity measures is a more cost-effective solution. As mentioned in the Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023 by IBM, the average data breach cost is about USD 4.45 million globally. Clearly, investing in cybersecurity beforehand is a smarter and more economical choice.
Alongside financial expenses, cyber attacks also impede business continuity. Some cybercriminals focus on disrupting network traffic and rendering services inaccessible. Others may encrypt your files and demand a ransom to decrypt your information.
Cybersecurity protects parties’ reputations and maintains trust. Unfortunately, security breaches can damage your business reputation and lead to loss of sales or customers. Additionally, legal consequences like regulatory sanctions or fines could result.
Conclusion
To sum up, IT professionals must follow the top 10 Cybersecurity best practices to protect their organizations against cyber threats. Consistent effort and dedication to learning and improvement are necessary to maintain strong cybersecurity. Staying ahead in the constantly evolving threat landscape requires a proactive approach. IT professionals play a crucial role in enhancing their organization’s cybersecurity by following these best practices.
You can apply for the Cyber Security Analyst Professional Course to get detailed information in the field of cyber security.




