The importance of cybersecurity increases every day as more sophisticated cyber attacks occur, and organizations are allocating considerable resources to enhance security efforts. The worldwide cybersecurity market was worth US$ 238.13 billion in the last year and is projected to grow by 12,6% in 2024, according to a report published by Precedence Research.
Cybersecurity provides confidentiality, integrity, and availability of digital information. Learning cybersecurity helps individuals learn and understand the nature of various cybersecurity threats and develop mitigation strategies. Cybersecurity enables individuals to protect data, address vulnerabilities, maintain business continuity, and manage sources.
Cybersecurity jobs are in high demand, and cybersecurity salaries are quite competitive. Having a comprehensive education and earning relevant cybersecurity certifications through a cybersecurity course boosts technical skills and helps professionals defend cyberspace against the threat landscape. Enrolling in a cyber security bootcamp and employing cybersecurity best practices help professionals become competitive in the market and secure a job quickly.

What Is Cyber Security?
Cybersecurity is the process of protecting data, networks, and systems against cyber threats. It is a comprehensive term that employs proactive actions and defense mechanisms to secure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of digital assets in cyberspace. The cybersecurity life cycle comprises fundamental stages such as identification, protection, detection, response, and recovery, according to the NIST Cybersecurity Framework.
Why Is Cybersecurity Important?
Cybersecurity is important for improving the security posture of the organization and protecting personal or sensitive data. It establishes strategies, policies, and best practices to defend against the threat landscape. Cybersecurity maintains business continuity, trust, and reputation. It sets professional standards and complies with regulations. Investing in cybersecurity reduces costs and helps avoid legal penalties.
Cybersecurity assesses vulnerabilities and manages risks, which reduce the attack surface. Similarly, cyber security salaries are quite competitive. For example, the median annual pay for all U.S. workers is about US$ 58,034, while the 2023 Median wage for cybersecurity analysts is US$ 120,360, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics.
What Are the Types of Cybersecurity?
There are many forms of cybersecurity that address different needs in the threat landscape. Here are the 9 main types of cybersecurity to consider:
- Information Security
- Network Security
- Application Security
- Endpoint Security
- Mobile Security
- Infrastructure Security
- Cloud Security
- Zero Trust Security
- IoT Security
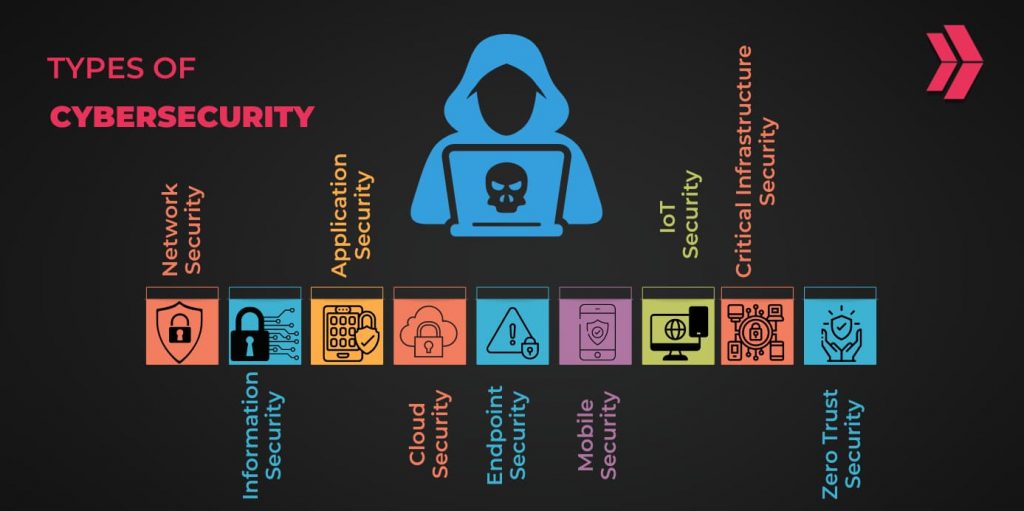
All of which play a crucial role in safeguarding against various threats and vulnerabilities across the different types of cybersecurity.
Information Security
Information security is the core of cybersecurity jobs. It ensures the safety of digital information by implementing security protocols such as encryption, password management, access control, system configuration, data backups, and focused user training.
Network Security
Network security is the combined efforts to segment the networks, implement the least privileges, restrict user access policies, and utilize cybersecurity tools like IPS/IDS, firewalls, SIEM tools, and EDR solutions.
Application Security
Application security safeguards software, especially web or mobile applications, by testing and identifying vulnerabilities, using strict authentication policies, employing secure coding techniques, and effective patch management.
Endpoint Security
Endpoint security protects end users such as computers, mobile devices, or servers from cyber intrusions. Endpoint security is the last line of defense, and using EDR, antivirus, anti-malware tools, and Mobile device management (MDM) policies improves overall security.
Mobile Security
Mobile security maintains the digital safety of laptops, tablets, and smartphones by implementing strong authentication and encryption, mobile device control, and patch management to defend mobile devices against cyber threats.
Infrastructure Security
Infrastructure security protects critical systems and resources and is vital for business continuity. It requires efficient inventory management, continuous monitoring, detailed plans, supply chain management, and authentication protocols.
Cloud Security
Cloud security is gaining more importance as more users rely on cloud services daily. Cloud security protects data, infrastructure, and applications by leveraging identity and access management (IAM), encryption, proper configuration, and cloud firewalls.
Zero Trust Security
The zero trust policy provides an extra layer of security to enhance overall safety. It doesn’t automatically trust any user and always verifies access with the least privilege, which eliminates possible risks. This concept offers better control and visibility over cyberspace.
IoT Security
The Internet of Things (IoT) security is becoming more critical as many IoT devices are vulnerable to cyber attacks with weak security measures. IoT security can protect sensitive assets and reduce the attack surface by changing default settings, regularly updating applications, and using strong passwords.
What are the Types of Cyber Attacks?
Threat actors use various methods and techniques to breach cyber defenses. Here are the 4 main types of cyber attacks:
- Malware Attacks:
Malware attacks employ malicious software such as viruses, worms, trojans, rootkits, fileless malware, and keyloggers to disrupt systems or steal information. Malware attacks increased by 30% in the first half of 2024 compared to the same period last year, according to the 2024 SonicWall Mid-Year Cyber Threat Report.
- Injection Attacks:
Attackers exploit vulnerabilities by injecting code or commands into applications. SQL Injection accounts for 23.4%, and Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) is 19.1% of all security breaches in 2023, according to Statista Report. Similarly, command injection and LDAP injection are among the most popular injection attacks.
- Social Engineering Attacks:
Threat actors manipulate users to compromise sensitive information by hacking human psychology. Phishing is the leading threat vector in social engineering techniques and had a 58.2% increase compared to the last year, according to Zscaler ThreatLabz 2024 Phishing Report.
- DDoS (Denial of Services) Attacks:
DDoS attacks overwhelm the target with excessive traffic from many different sources and disrupt normal traffic and functions. In the first quarter of 2024, DDoS attacks nearly increased by 50% compared to the previous year period, according to Cloudflare.
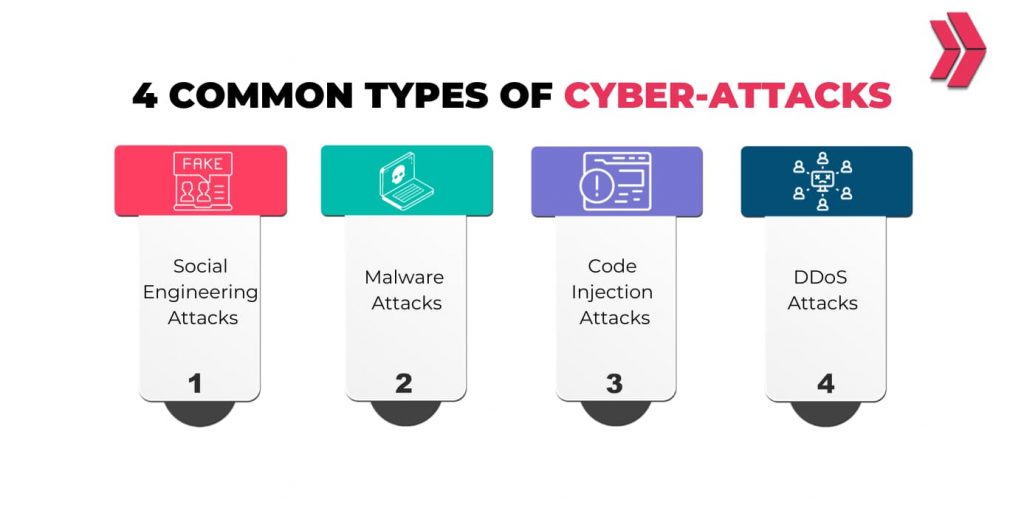
Understanding these 4 types of cyber attacks will improve the organization’s security posture, help secure entry-level cyber security jobs, and advance in a cybersecurity career.
What are the Common Cybersecurity Threats?
As technology evolves, threat actors use sophisticated techniques to launch cyber attacks. Here are the 7 common cybersecurity threats:
- Social Engineering Attacks
- Phishing Attacks
- Malware Attacks
- Ransomware Attacks
- Injection Attacks
- Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks
- DDoS Attacks
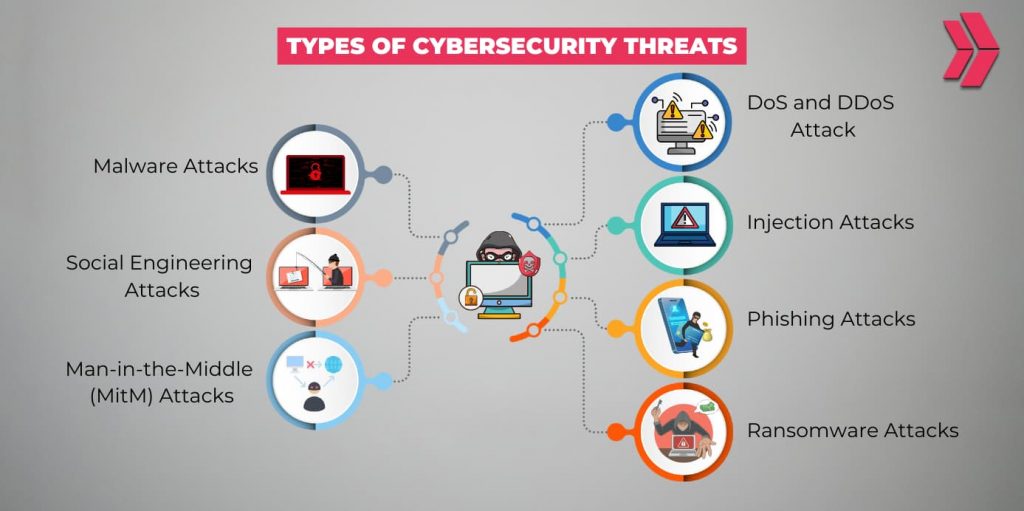
Understanding these vulnerabilities is crucial for defending against the most prevalent cybersecurity threats.
Social Engineering Attacks
Social engineering exploits human nature, and attackers utilize these techniques in 98% of all attacks, according to a report by PurpleSec 2021. The most common types of social engineering involve phishing, vishing, smishing, whaling, Business Email Compromise (BEC), and watering hole attacks.
Phishing Attacks
Phishing is the most prominent attack vector in cybersecurity, which falls under social engineering. Phishing is the gateway for other types of intrusions, and nearly 90% of cyber attacks start with a phishing form, according to the Annual State of Email Security Report published by Cofense in 2024.
Malware Attacks
Malware attacks are very dangerous and result in a 40% success rate of data leakage, according to the Cybersecurity Threatscape: Q2 2022 report published by Positive Technologies. Attackers use malicious software to disrupt, modify, encrypt, or exfiltrate information.
Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware is deemed the most dangerous malware attack because it causes financial and reputational damage. 84% of organizations agreed to pay the ransom demand after a security breach, and 78% of them had a second attack after restoration, according to Ransomware: The True Cost to Business 2024 report published by Cybereason.
Injection Attacks
Injection attacks are the third most severe web application security threat, according to the OWASP Top 10:2021 project. Cyber intruders can inject a harmful payload into a program or query to retrieve, modify, or delete data in the target. SQL injections are the most prevalent threat in all injection attacks.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks
Man-in-the-middle attacks intercept, eavesdrop, or manipulate the traffic between two parties. MitM attacks are on the rise, and in the first quarter of 2023, there was a 35% increase compared to the same period of the previous year, according to Cofense intelligence statistics. Session hijacking, wifi eavesdropping, and email hijacking are among the most common attacks.
DDoS Attacks
DDoS attacks disrupt the target with excessive traffic, which tests and indicates what is cyber security posture is. There is a 50% increase in the first quarter of 2024 compared to 2023 Q1, according to the 2024 Cloudflare DDoS Threat Report. DDoS attacks comprise 3 main types: volumetric, protocol, and application layer attacks.
What are the Cybersecurity Best Practices?
Here are the top 10 cybersecurity best practices:
- Encrypting Data
- Using Strong Passwords
- Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Utilizing Cybersecurity Solutions
- Employing Cybersecurity Frameworks
- Keeping Software Up to Date
- Being Vigilant Against Social Engineering Attacks
- Backing-up Data
- Educating Employees
- Embracing Continuous Learning

To ensure that organizations stay protected, it is crucial to adhere to cybersecurity best practices.
Encrypting Data
Data encryption provides the confidentiality of sensitive information by using encryption algorithms, keys, and emerging technologies.
Using Strong Passwords
A robust password policy is vital in preventing unauthorized access and safeguarding data privacy in cyberspace.
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication offers additional security measures to preempt and prevent security breaches.
Utilizing Cybersecurity Solutions
Technological tools and technologies such as firewalls, IPS/IDS, SIEM, and WAF enhance security posture.
Employing Cybersecurity Frameworks
Cybersecurity frameworks are the blueprints for threat management that provide standards, best practices, and guidelines to thwart digital attacks.
Keeping Software Up to Date
Professionals should regularly update software and manage patches to identify and fix security vulnerabilities and boost performance.
Being Vigilant Against Social Engineering Attacks
Social engineering attacks are the springboard to other attacks, and recognizing these threats will mitigate possible intrusions.
Backing-up Data
Regular backups maintain business continuity and reputation, reduce downtimes, and save energy and time during cyber attacks and failures.
Educating Employees
Training is indispensable in the fight against cyber attacks. Additionally, obtaining a cybersecurity certification improves technical capabilities to better prepare for digital threats.
Embracing Continuous Learning
Professionals should engage in ongoing learning for networking and collaboration opportunities, stay current with the latest developments, and enhance professional skills to excel in the threat landscape.
How to Build a Career in Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity jobs are in high demand, and there are 3 main steps to building a successful career. First, professionals should have proper training; second, obtain relevant certifications; third, have hands-on experience.
Various cybersecurity career path opportunities are available in the field, and the cybersecurity salary, even in entry level cybersecurity jobs, is quite competitive and satisfactory.
What Are Key Cybersecurity Certifications for Career Enhancement?
Earning cybersecurity certifications validates the expertise and skill in the field. Enrolling in a cyber security course offers an excellent opportunity to earn these credentials. Here are some key cyber security certifications: CompTIA Security+, Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), Systems Security Certified Practitioner (SSCP), Certified Information Security Manager (CISM), and Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP).
What Benefits Do Cybersecurity Bootcamps Offer for Skill Development?
A cyber security bootcamp offers 5 main benefits for skill development: First, a bootcamp is more affordable than traditional education. Second, it uses a job-oriented and focused curriculum. Third, a bootcamp provides career coaching during the course. Fourth, it employs hands-on training to reinforce theoretical knowledge. Fifth, a cyber security bootcamp offers a flexible schedule that lets participants keep their full-time jobs.
What Are the Essentials of Cybersecurity Training for Beginners?
Cybersecurity professionals should acquire comprehensive cybersecurity training, obtain relevant certifications, gain practical experience, and follow the latest trends. In addition, some other essentials of cybersecurity training for beginners include prioritizing continual education and self-improvement, establishing a network, and engaging in community activities to excel in cybersecurity.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity is essential to safeguard information, enhance overall security posture, maintain business continuity and reputation, and save time and resources. The four prominent categories of cyber attacks are malware, injection, social engineering, and DDoS attacks.
Cybersecurity experts can preempt and mitigate cyber attacks by employing best practices such as data encryption, strong password and MFA usage, data backups, robust frameworks, update, and patch management, leveraging technological tools, and ongoing education.Building a successful career in cybersecurity involves 3 main steps: extensive cybersecurity training, relevant certifications, and hands-on experience. Cybersecurity jobs are in high demand, and a cyber security bootcamp is beneficial for understanding the latest concepts and developing new skills. A cyber security course is vital for safeguarding cyberspace and landing a job quickly.




